1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
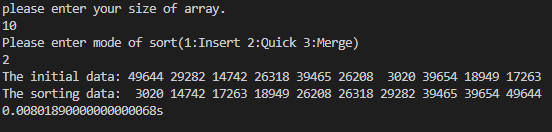
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>//srand()
#include<ctime>//time函式
#include<iomanip>//setw(),空格函式
#include<windows.h>//cpu頻率
// #include<algorithm>//swap()函式
using namespace std;
class Sorting
// sorting類別包含三個sort
{
public:
void InsertSort(int *initList,const int n);
void MergeSort(int *initList, const int n);
void QuickSort(const int left, const int right);
Sorting(){ }//default函式,當呼叫一次sort型別就會construct一次
void print(int n);//此print是從1~n,是針對tree的情況下使用
// tree不會用到arr[0]方便對照
void printAll(int n);//printAll是從0~n
~Sorting(); //destructor,解構
void eqPtr(int *a)//把main裡面的pointer給class裡,讓所有sorting都可以使用
{
ptr = a;
}
private:
int *ptr;
void swap(int &a,int &b);
void merge(int *initList, int *result, const int L, const int m, const int n);
void MergePass(int *initList, int *result, const int n, const int subSize);
};
int main()
{
int size;// array size
int mode;//sorting 的模式
srand(time(0));//宣告亂數
Sorting answer;
LARGE_INTEGER startTime, endTime, fre;
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&fre);//取得CPU頻率
double times;
cout << "please enter your size of array." << endl;
cin >> size;
int *temp = new int[size + 1];
int *adTemp = new int[size + 1];
adTemp[0] = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < size;i++)
{
temp[i]=(long long)((double)(rand()*49999)/RAND_MAX)+1;
// (long long)用來好取後20位數
// 不能用rand%50000,因為只有到32767
//temp[i] = randint(1, 50000);
}
temp[size] = INT_MAX; //in order not to out of range
// 將暫存器的最後一個位置=int裡的最大值=2^31-1
//避免i++超過array size
for (int j = 0; j < size;j++)
{
adTemp[j + 1] = temp[j];
}
cout << "Please enter mode of sort(1:Insert 2:Quick 3:Merge)" << endl;
cin >> mode;
cout << "The initial data: ";
QueryPerformanceCounter(&startTime);//開始啟用位置
if(mode == 1)//insert
{
answer.eqPtr(temp);
answer.printAll(size);
answer.InsertSort(0,size);
cout << "The sorting data: ";
answer.printAll(size);
}
if(mode == 2)//quick
{
answer.eqPtr(temp);
answer.printAll(size);
answer.QuickSort(0, size);
cout << "The sorting data: ";
answer.printAll(size);
}
if(mode == 3)//merge
{
answer.eqPtr(adTemp);
answer.print(size);
answer.MergeSort(adTemp,size);
cout << "The sorting data: ";
answer.print(size);
}
QueryPerformanceCounter(&endTime);// 時間結束的地方
times=(double)(endTime.QuadPart-startTime.QuadPart)/fre.QuadPart;
cout << fixed << setprecision(20) << times << "s" << endl;
// fixed 是小數點後,setprecision(20)是20位
}
void Sorting::print(int n)
{
for (int i=0; i <= n;i++)
{
cout << setw(5) << ptr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//自己定義swap函式
void Sorting::swap(int &a,int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b=temp;
}
//解構式
Sorting::~Sorting()
{
delete[]ptr;
}
//Insert Sort:
void Sorting::InsertSort(int *initList,const int size)
{
for (int i = 1; i < size;i++)
{
int key = ptr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while(key < ptr[j] && j >= 0)
// 這裡的j記得是>=0
{
ptr[j + 1] = ptr[j];
j--;
}
ptr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
//Quick Sort:
void Sorting::QuickSort(const int left,const int right)
{
if(left<right)
{
int i=left,
// j不會小於array size因為碰到樞紐就會break(樞紐從arr[0]開始)
j=right+1,
// j設為最大值(自己定義的int_max),避免i超過array size
pivot=ptr[left];
// 樞紐設為第一位
do{
do i++; while (ptr[i] < pivot);
//選左邊比樞紐大的
do j--; while (ptr[j] > pivot);
//選右邊比樞紐小的
if(i<j) {swap(ptr[i], ptr[j]);}
} while (i < j);
swap(ptr[left], ptr[j]);
QuickSort(left, j - 1);//樞紐左邊的QuickSort
QuickSort(j + 1, right);//樞紐右邊的QuickSort
}
}
//Merge Sort:
// merge:實作2個list合併
void Sorting::merge (int *initList,int *result,const int L,const int m,const int n )
//m=中間
{
int i1, i2, iResult;//兩個數列分為前半後半,iresult是位置
for (i1 = L, iResult = L, i2 = m + 1; i1 <= m && i2 <= n;iResult++)
{
if(initList[i1]<=initList[i2])//較大的放進result且將位置往後移
{
result[iResult] = initList[i1];
i1++;
}
else
{
result[iResult] = initList[i2];
i2++;
}
}//上述迴圈結束會有(左或右)一端數列剩下
if(i1<=m)//copy data避免資料消失,m=中間
{
for (; i1 <= m;i1++)
{
result[iResult] = initList[i1];
++iResult;
}
}
else if(i2<=n)//copy data避免資料消失,n=最右邊
{
for (; i2 <= n;i2++)
{
result[iResult] = initList[i2];
++iResult;
}
}
//上述兩個if中只會有一個成立
}
// mergepass:幫merge計算中間和尾巴
void Sorting::MergePass (int *initList,int *result,const int n, const int subSize)
{
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= n - 2 * subSize + 1;i+=2*subSize)
{
merge(initList, result, i, i + subSize - 1, i + 2 * subSize - 1);
// 一倍mergesize跟兩倍mergesize,sub-1是因為剛剛arr[+1]
}
if((i+subSize-1)<n)
{
merge(initList, result, i, i+subSize - 1, n);
}
else
{
for (int j = i; j <= n;j++)
{
result[j] = initList[j];
}
}
}
// mergesort是呼叫函式
// mergesort -> mergepath->merge
void Sorting::MergeSort(int *initList,const int n)
{
int *temp = new int[n + 1];
for (int L = 1; L < n; L *= 2)
{
MergePass(initList, temp, n, L);//選mergePass的範圍
L *= 2;//範圍conquer*2
MergePass(temp, initList, n, L);
}
ptr = initList;
delete[] temp;
}
//Merge Sort End
void Sorting::printAll(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n;i++)
cout << setw(5) << ptr[i] << " ";
cout<<endl;
}
|